SiO2 – this is the chemical name of the base material for oscillating quartz crystals. The formula shows that it is composed of only two elements: silicon and oxygen. We also find SiO2 in its crystalline form in the nature: as natural rock crystals. Here, the question arises:
Are real rock crystals used for production of oscillating quartz crystals?
Let’s take a closer look at the first steps in the quartz production:
Real rock crystals once formed the basis of quartz crystals. However, for the economic production of the components, highly pure rock crystals are needed. At the beginning of quartz production, real rock crystals were used and, therefore, examined and sorted by hand according to their purity. In this form, however, rock crystals are rarely available in nature.
The artificial quartz production
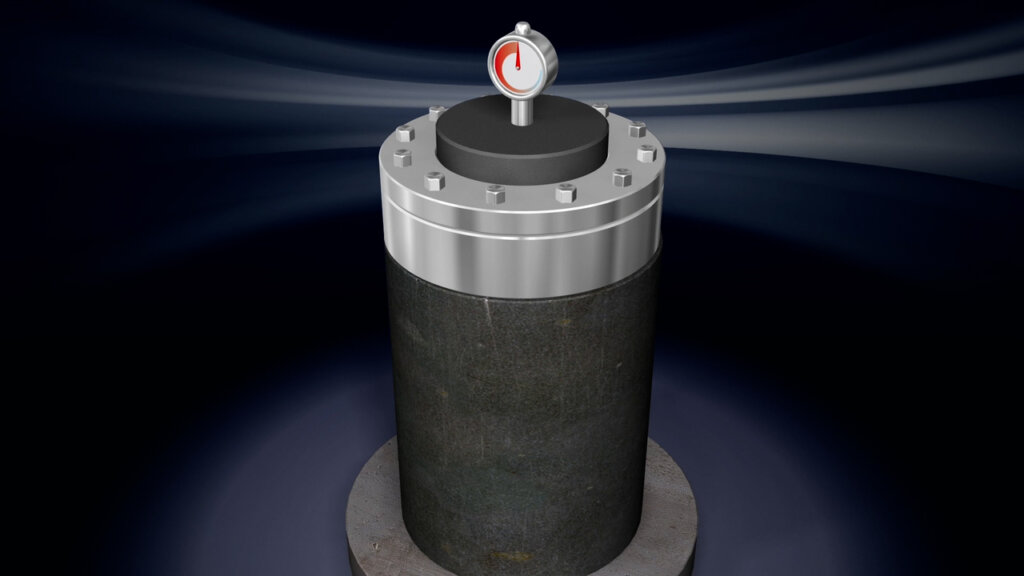
In order to meet the quality requirements for the quartz material, quartz crystals are nowadays produced artificially in so-called ‘autoclaves’. The autoclaves work according to the principle of hydrothermal synthesis. Broken crystal fragments are dissolved in an alkaline solvent. Thus, crystals can be grown in a controlled manner. The autoclave is sealed hermetically and is heating up to temperatures of 350 °C to 400 °C. It works with pressures around 1500 bar. The advantage? Artificial crystals have a regular lattice of SiO2 – a good condition for high-quality quartz crystals.

How the quartz crystal grows
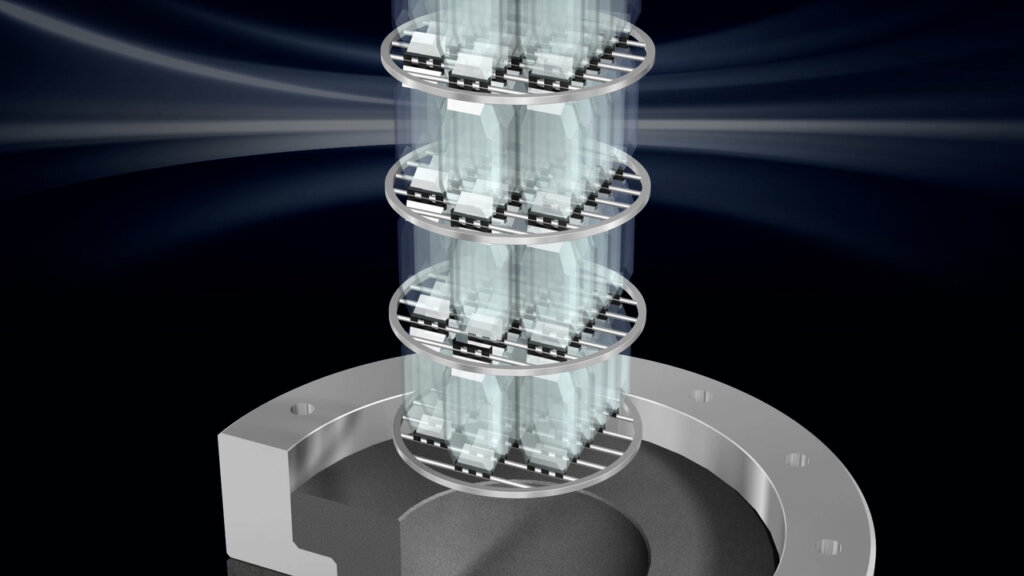
The lower part of the autoclave, the pressure vessel, is filled with water, mineralizer additives and SiO2. So-called ‘seed crystals’ are placed in the upper part. In the autoclave, the temperature rises. It is heated from the bottom, so that there is a temperature difference between the lower and upper chambers. The parts dissolved in the lower area settle on the seed crystals. The growth rate is determined by temperature and pressure. Depending on the values, a growth of the quartz of 0.2 to 1 mm per day is possible. The slower the growth, the higher the quality of the result.
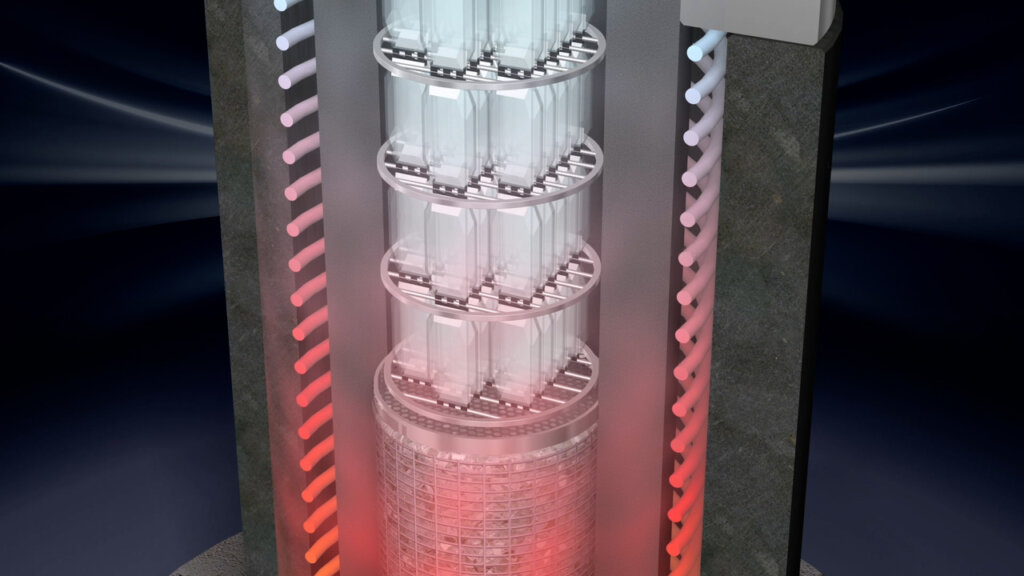

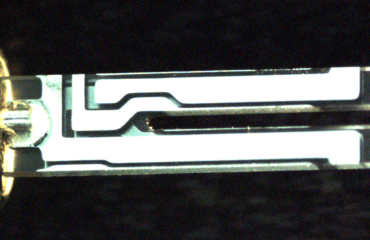
After about 40 to 80 days, the ‘alpha’ crystal is produced, which can even weigh several kilos. In the next step, individual blanks are cut out of the quartz wafers. Here, different cutting angles have to be considered. The seedling is also cut out in the process and is used again for quartz production in the autoclave.
More articles about this topic:
Quartz production process: from quartz block to quartz blank
From assembly to the final product – the last stages in the quartz manufacturing process


 Deutsch
Deutsch