
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries (Li/SOCl₂) belong to the lithium primary cell family. Unlike lithium ion or lithium polymer batteries, these cells cannot be recharged once they have been discharged. However, due to their long lifetime, this characteristic is of little importance in everyday use. In fact, lithium thionyl chloride batteries supply power to applications for several months or even years before they need to be replaced.
Li/SOCl₂ batteries have been an integral part of Jauch’s battery portfolio for many years. This year, the portfolio expanded to include batteries from Jauch’s own brand. The most important properties of this cell chemistry are briefly presented below.
High Voltage – High Safety
Lithium primary cells, which also include lithium iron sulfide or lithium manganese dioxide batteries, usually have a cell voltage between 1.5 volts and 3 volts. However, the cell voltage of a lithium thionyl chloride battery is significantly higher than these values: with a voltage of 3.6 volts. At this value, the battery performs to the level of lithium ion batteries. This voltage level is kept constant by the battery over almost the entire discharge period – an absolute unique selling point of lithium thionyl chloride cell chemistry.
In terms of energy density, Li/SOCl₂ batteries are also superior to all other primary cells. Values up to 710 watt hours/kilogram are possible.
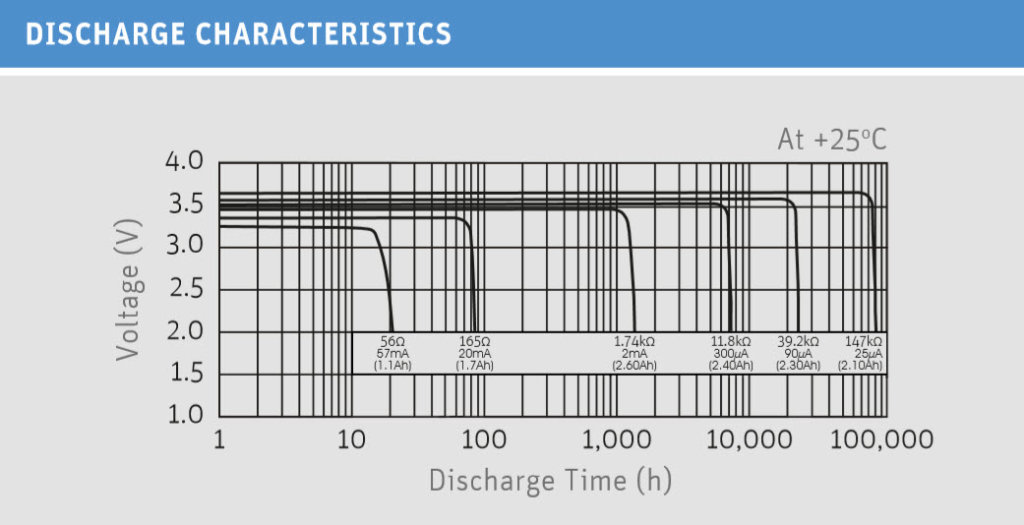
Low Currents – Wide Temperature Range
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries are used wherever low currents are required over a long period of time. Typical applications are for example locking cylinders, timers, toll systems or all kinds of metering applications. The high energy density of the thionyl chloride cells ensures that these applications can be operated for several months or even years without having to replace the battery.
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries are designed for use in a temperature range between -60 and +85 degrees Celsius. Particularly noteworthy is the performance of the cells at low temperatures. Even at double-digit minus temperatures, the cells deliver a constantly high voltage.
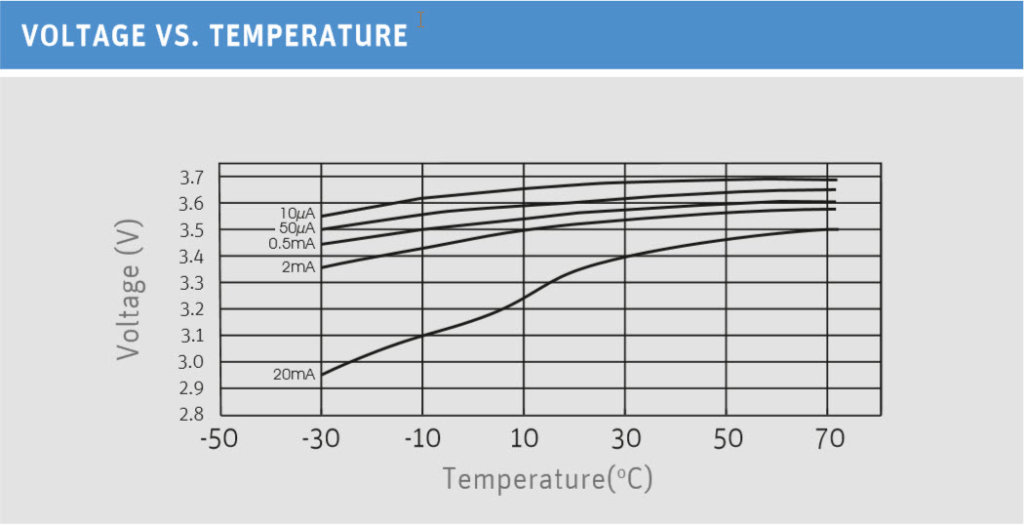
Passivation of the Battery
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries are very durable and have a very good shelf life. The self-discharge rate of only 1% per year speaks for itself.
The longevity of lithium thionyl chloride batteries is due to the chemistry of the cell. Unlike other lithium primary cells, the lithium thionyl chloride cell undergoes a chemical reaction between the lithium anode and the electrolyte. As a result, a protective film forms over the lithium anode, which impedes the ion flow between the anode and cathode. This is referred to as “passivation” of the battery cell.
This phenomenon has advantages and disadvantages. On the one hand, passivation is responsible for the low self-discharge rate of the battery. On the other hand, the resulting protective film initially impedes the current flow when the battery is put into operation. The protective film gradually fades away as the battery continues to operate. However, it forms again as soon as the battery stops drawing current. For this reason, lithium thionyl chloride batteries are particularly suitable for applications with low power consumption. The power requirement of the application can be constant or pulse-shaped.
The Bobbin-Type Cell Construction
Lithium thionyl chloride batteries are available in numerous sizes and designs. No matter what variation your application requires, the core properties: high voltage, high energy density and long life, stay the same.
The “Bobbin-type” construction has established itself as the most frequently used cell construction method. This design, which is also used in the cells of Jauch’s thionyl chloride batteries, is characterized by a high level of safety and a long service life. These batteries deliver currents of up to two Amperes.

Jauch’s battery portfolio includes various Li/SOCl₂ batteries. An overview of the entire Jauch portfolio of lithium thionyl chloride batteries can be found here.
Our battery experts will be happy to advise you on which of these cells is best suited for your application. Equipped with the expertise from countless successfully completed projects, our experts will also find the perfect solution for your requirement profile and will advise you on request directly at your site.
You already know what you need? Then order your samples here!


 Deutsch
Deutsch 

It is amazing to visit your blog! Thanks for sharing valuable information about Lithium thionyl chloride batteries, Keep up the great writing.
Dear Sir,
Please tell us the life in years of Lithium thionyl chloride battery if it is stored unused for long periods of time
Ganapathy
Hi there,
first of all tahnks for your comment!
I imagine many readers would ask the same question. Unfortunately, it cannot be answered in a generalized way. It’s very difficult to make reliable statements about long-term behavior of lithium thionyl chloride batteries as there are many external factors involved, e.g. temperature of storage.
So, what can be stated is that lithium thionyl chloride batteries of “Jauch”-brand do have a self-discharge of 1% per year if stored at 20 degree Celsius.
However, as storage time increases, so does the passiviation of the battery.
Hope this Information will help you!
Best
Pascal
Dear Sir,
I’m curious, why with the lower discharge currents (uA) the capacity of the battery is lower than for example 1 mA discharge current?
Does the graph can be interpreted, that self-discharge current of the battery is higher than usable current in device?
Hi Mr. Pawelec,
thanks for your comment!
The reason why capacity is lower with lower discharge current is due to the self-discharge of the battery. Lower discharge current means a longer service life of the battery resulting in a stronger effect of self-discharge on capacity than with higher discharge current and shorter service life.
Hope this will help you.
Best Regards
Pascal
Since these batteries cannot be recharged how do you dispose of them?
Hi Mr Young,
thanks for your comment!
The proper disposal of lithium thionyl chloride batteries is regulated by national legislation. Please follow the regulations valid in your country.
In addition, when disposing of the battery, make sure that the negative and positive terminals are completely shielded with insulating tape or other insulating material. Finally, even discharged batteries have a residual electrical capacity, so that if the poles come into contact with metal, short circuits or similar events can occur.
Hope this will help you!
Best Regards
Pascal
One of my sons showed me this website. Imagine my surprise. My great grandfather came to the United States during World War 1, from Schwenningen. I am 74 years old and have never met another family named Jauch. I lived in Muenchweiler, Rodalb in 1966 and 1967 when I was in the US Army. My prayers to all named Jauch during this time of pandemic.
I am using lithium thionyl chloride batteries in a circuit where constant current in the range of micro amp. is required to keep my clock up
through RTC chip. However the same batteries are also used in the tamper detection circuit where during tamper signal getting activated
a pulse of 25mA is required.
Since already constant current in the range of micro ampere is drawn to keep my clock up, do I require any de passiviation process
to be implemented for the batteries.
Hi Mr. Banerjee
first of all, thanks for your comment!
Unfortunately, there is no general answer to your question. The required de-passivation currents depend on the battery you are using. Batteries of different manufacturers differ from each other and thus may require different de-passivation currents. There are also differences between different battery types from the same manufacturer.
But to give you a little orientation: For our ER14250 Jauch batteries, for example, a continuous load of 15 micro amp. is sufficient for de-passivation.
Hope this will help you a little 😊
Best Regards
Pascal
Hello
I am working in a metering company that uses the Li Thionyl Chloride batteries, i was wondering is there a way to check the battery capacity before it is implemented in the product
Hi Mr. Verma,
thanks for your question!
Unfortunately, the only way to check the capacity of a lithium thionyl chloride battery is by discharching it 🙁
So the best thing you can do to ensure a reliable power supply of your meters is to choose a high-quality battery manufacturer.
Best Regards
Pascal
Hello Pascal,
Just to add Siddharth’s query. How are manufacturer making sure about claimed capacity. Are they testing it before supplying??
Hi Prasanna,
thanks for your comment!
In most cases, battery production is automated to large extent. Each cell is subjected to various quality tests during production. If a cell does not meet the defined standards, it is automatically sorted out.
As far as capacity is concerned, manufacturers usually take a random sample from each batch and check the capacity by discharging.
Best Regards
Pascal
Hi Pascal,
I am investigating whether or not an AA Lithium Thionyl Chloride cell will be suitable for use in an instrument that draws up to 90mA for a few minutes when it is use, and spends the rest of its time turned off. The data for these cells is generally given in the uA up to a few mA range, although the discharge curves in this article do have a line for 57mA which is approaching my desired operating point.
Please can you tell me where I can find information about how the cell will perform under loads up to 100mA? What will the drawbacks be? Will it still offer significantly higher energy yield than an alkaline under similar conditions? Are there any safety issues?
The voltage and dimensions make this cell ideal for my application if it can cope with the higher currents.
Thank you for your help,
James
Hi James,
thanks for your comment!
In general, AA lithium thionyl chloride batteries can deliver currents of 90 mA and more. Our ER14505J cell for example delivers 100mA continuous current max. Please check the datasheet: https://www.jauch.com/de-INT/produkte/batterie_technologie/getPrm/batteries/lithium%20thionyl%20chloride%20batteries/
However, you’re saying that your instrument will be switched off most of the time, so you will have to deal with passivation of the battery. In lithium thionyl chloride batteries, there is a chemical reaction between the electrolyte and the lithium anode. As a consequence, a protective layer of lithium chloride crystals forms over the lithium anode.
This passivation layer over the battery’s anode obstructs the flow of current and thus provokes a drop in the operating voltage. With continuous operation, the passivation layer is gradually eroded, so the operating voltage raises to its normal level. However, the layer forms again if there’s no current drawn from the battery for a while.
The best way to prevent this is to ensure constant de-passivation currents being drawn from your battery. For an ER14505J battery, for example, a continuous load current of 30 µA is recommended. It is also possible to apply a weekly pulse current of 20mA over a duration of 10 seconds, or a monthly pulse current of the same intensity over a duration of 60 seconds.
You can find some additional information on passivation in this article: Passivation of Lithium Thionyl Chloride Batteries – Jauch Blog-Seite
Hope I could help you a little 😊
Best Regards
Pascal
hi,
i recycle used end of life gas meters and generate a large number of Lithium Thionyl Chloride batteries, these currently go for incineration. is there a safe process to recycle/ dispose of the batteries?
the batteries are in various states of discharge.
cheers
Mick Young
Hi Mick,
thanks for your comment!
First of all, disposal of Lithium Thionyl Chloride batteries should always be done in accordance with applicable regulations, that vary from country to country. So, please check the legal background in your country.
Incinerating Lithium Thionyl Chloride batteries can be very dangerous, especially when they are not fully discharged! The Exposure of these cells to high temperatures or fire can cause the cells to vent and/or rupture.
As a consequence, you should NOT try to dispose/recycle those batteries on your own but turn to an authorized facility within your country instead.
Best Regards
Pascal
Hi Pascal,
thanks for your nice blog. I have one question, why Lithium Thionyl Chloride batteries cannot be recharged?
Kind regards,
Gang
Hi Gang,
thanks for your comment and sorry for the late answer!
Cells with metallic lithium, e.g. thionyl chloride cells should not be charged as the lithium is deposited dendritically and this can lead to internal short circuits and to the disintegration of the cell with the appearance of fire.
Best regards
Selina
Mr. Pascal,
Thanks a lot for sharing good information.
We would like to discharge these Lithium Thionyl Chloride batteries first and then recycling, what advice could you please give us? I would like to work on this project.
Best Regarding
Avez
Dear Avez,
thank you for your question. I just talked to one of our experts and this is what he said.
In the data sheet of your battery you can find the standard voltage and resistance. Then you know with which resistor you can discharge your batteries. It ist important to not use voltages that are too high.
I hope that this answer helps you.
Best regards
Selina
Hi –
Can two Lithium Thionyl Chloride batteries be wired in parallel?
Thanks,
Joe
Hi Joe,
yes, then can be wired in parallel.
Best regards
Selina
hi, my device uses 2 AA alkaline batteries in series resulting a voltage of nearly 3V for new batteries, and when it is nearly 2.1V, device transmits a low battery alert. Now I want to use a single Lisocl2 AA battery for the device.
I have read that the battery voltage would be constant(3.6V) up until the battery is empty. Is there a way to detect low battery condition during device operation?.
My device has a continuous drain of 0.3mA.
Hi Ravi,
After consulting with our expert, I have the following answer: With Lithium-Thionylchlorid Batteries the only possibility would be to use a coulomb counter which shows what has been taken out.
Kind regards
Selina