
Have you ever wondered why you have to recharge your smartphone battery at increasingly shorter intervals after 1 to 2 years of use? Of course, the phenomenon is not limited to the battery in the smartphone – every rechargeable battery inevitably loses storage capacity over time. But what is the reason for this? And how can the lifetime of a rechargeable battery be determined?
The service life of a battery indicates how long the battery can be used in a product before the tolerable loss of performance falls below a certain threshold. These values vary depending on the application. Accordingly, it is complex to give an exact lifetime for a battery in e.g. years.
Which parameters influence the service life of a battery?
The service life of a rechargeable battery depends on various factors. This includes all steps from storage to commissioning, as well as discharge and to a large extent the appropriate charging conditions. It is also related to the number of charge and discharge cycles. As life increases, there is a loss of capacity and an increase in the impedance (internal resistance) of the battery.
This is how the life of a rechargeable battery is determined
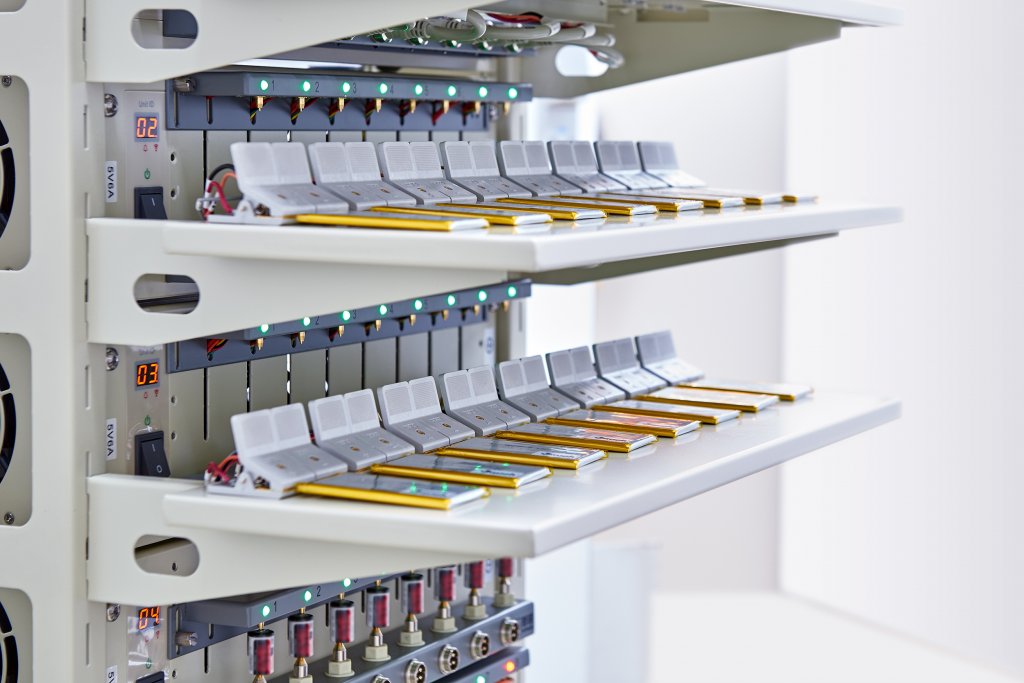

An indication of the service life is determined by the manufacturers by means of standardized cycles in the laboratory and with storage tests at various temperatures. Standardized cycles, which means that the cell is fully charged and fully discharged. The whole takes place at room temperature and the maximum currents according to specification. The decisive factor for the service life in cycles is, therefore, the charge conversion during charging and discharging. If the battery were not fully charged to 100 percent, the achievable number of cycles would end up being higher.
However, it should not be concluded from this that the battery should always be recharged immediately, after the smallest discharge. This is also referred to as trickle charge. The conditions of this handling lead to the battery being kept in a state of full charge almost all the time, which eventually leads to performance degradation and cell failure. In addition, there is a risk of extreme swelling and cell failure with lithium polymer cells and prismatic cells. With cylindrical cells, the trickle charge can cause abrupt failure.
However, the laboratory conditions under which the service life of rechargeable batteries is determined correspond in very few cases to the conditions of the reality of the application. This leads to the question:
What can we do to achieve the longest possible service life?
In this chapter, we will take a close look at the measures that can be taken by users and end customers to treat batteries as gently as possible and to positively influence their service life.
First of all, the temperatures during loading must be maintained according to specification. This is because excessive charge currents at temperatures below 15°C can cause lithium plating on the anode side of some types. This, in turn, can lead to a drop in capacity and, in the worst case, to internal short circuits with a fire hazard. At the same time, too high temperatures should also be avoided. For many cells, charging in the temperature range of 0°C to 45°C is considered optimal, taking into account the currents.
The storage of the cells or batteries also influences the service life. Storage at room temperature or lower is recommended. However, it is essential to avoid temperature fluctuations, which lead to a reduction in service life. So, if possible, the batteries should be stored in a climate-controlled environment to have as little impact as possible on their lifespan.
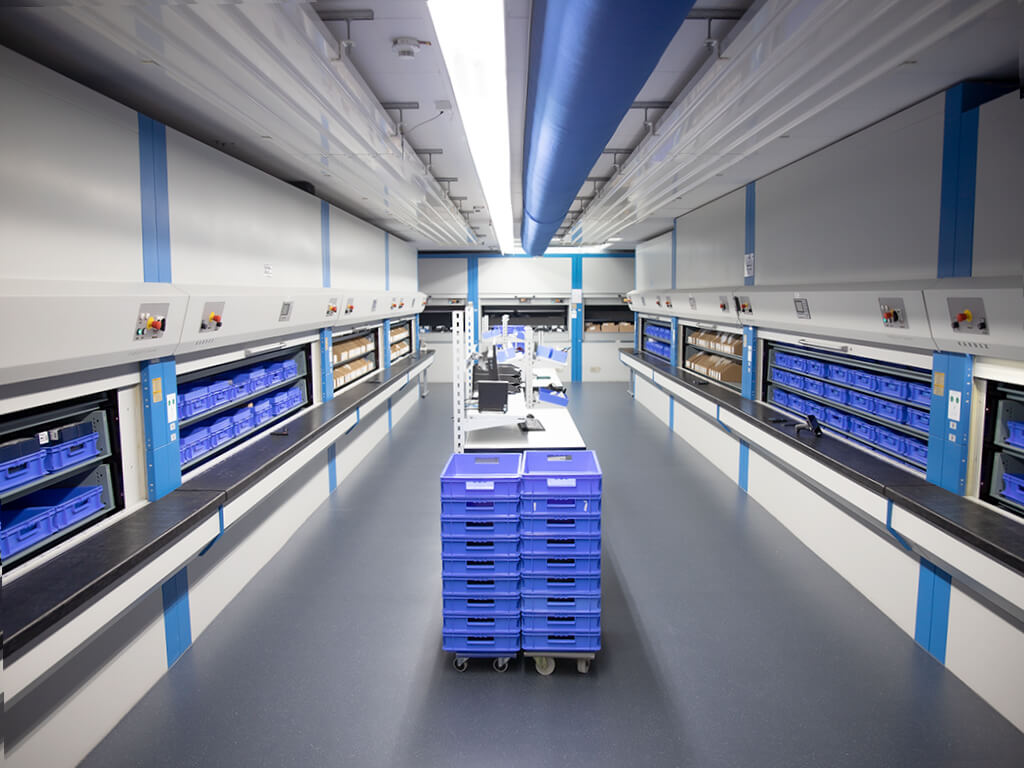

It is obvious that the FIFO principle (First-In-First-Out) should be strictly adhered to in the warehouse. Cells are ideally checked periodically during charging and recharged if necessary.
As a further measure to extend the life of a rechargeable battery, a lower charge cut-off voltage is recommended. This is especially true for batteries that operate at higher temperatures. In the case of a standard lithium-ion or lithium-polymer battery, in this case the battery is only charged to 4.0 or 4.1 volts instead of up to 4.2 volts.
These “handlings”, i.e. instructions for storage and installation in the device, should be provided to every user of batteries.
How can the end customer treat his batteries gently to achieve the longest possible service life?
With regard to storage, it is also important for end customers that the battery, or the device, should not be stored and operated at higher temperatures (e.g. in direct sunlight or under the windshield in intense sunlight).
On the other hand, it has a positive impact on the service life if the end customer only charges his device up to 90 percent (especially when high temperatures prevail).
If possible, batteries should not be charged continuously, e.g. overnight. This keeps the battery in an unfavorable state of full charge and leads to a reduction in service life. So better unplug the phone overnight (or use a phone with a smart charger that avoids continuous charging) 😉.

Batteries should also be protected from deep discharge. It is, therefore, best to charge the devices to at least 50 percent before not using them for a longer period of time. Do not store unloaded.
And finally: use supplied chargers/power supplies. These are designed by the manufacturer for the application and its battery and ensure that the maximum currents are not exceeded during charging and that there is no safety risk during the charging process.
Do you have questions or are you looking for the right battery for your application? Our experts will be happy to help you.


 Deutsch
Deutsch 



Hello,
Thanks for sharing information with us..